As video editors, we’re well aware of the impact that resolution has on the quality of a video. As much as we try to set the right bitrate, framerate, or aspect ratio, it all goes in vain if the whole thing is recorded with very low video quality.
But, in the majority of cases, the editors aren’t the ones who shoot the footage. That is why, it’s very important for those seeking video editing services to know the right resolution to use before hitting ‘record’.
Before we get to learning what’s the best quality setting to use, we’ll learn what video resolution means and how it differs from other important quality factors.

What is video resolution?
Video resolution is the number of pixels present in each frame of video footage. The pixel count, arranged horizontally (width) and vertically (height), is directly responsible for the amount of visual detail in a frame. So, logically, if there are more pixels in every frame of a clip, the more the visual detail (or quality).
An important point to remember is that, after shooting, you may easily go from high-resolution to low-resolution, but it’s impossible to do the opposite. So, regardless of what resolution you actually want, shoot at a higher resolution so that you can adjust it to suit different formats.
What’s the difference between video resolution, frame rate, aspect ratio, and bitrate?
| Frame Rate | Bitrate | Aspect Ratio | Video Resolution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Frame rate is the number of frames shown in a span of one second. | Bitrate is the number of bits (data) in a video that can be transferred or processed within one second. | Aspect ratio is the measure of a frame’s width in comparison to its height. | Video resolution is the number of pixels that are present within a single frame. |
| Measurement | fps (frame rate per second) | fps (bits per second) | W:H | pixels (w x h) |
| Impact on video quality | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
Types of video resolution
When you record, you always do so with a clear idea of where it will be played. So, if you’re shooting a movie, you know that it will appear in cinemas, on television, and on streaming platforms. Each of these has a recommended resolution to ensure quality footage. So, you’ll need to record at a higher resolution and create copies for each platform with the appropriate visual quality during post-production.
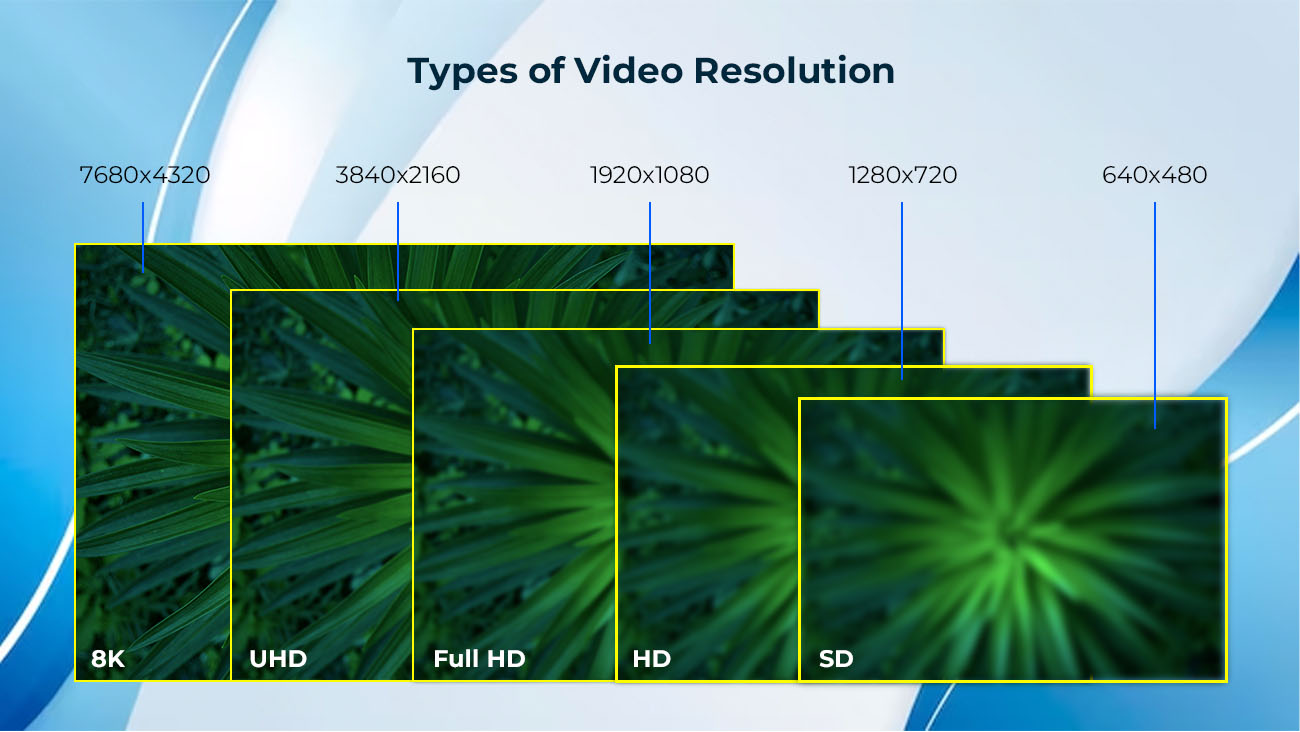
So, what are the different types?
SD or Standard definition
Before smartphones and tablets, this was the best resolution for videos from the early 1950s to the mid-2000s. It was used for television, VHS, DVDs, and even the early digital videos. Hence, the term ‘standard’ was used for this quality type.
Even when viewed today, SD videos still look good and clear, but it’s clear that there isn’t that much detail. The reason for this is because this video resolution size is only 640×480 pixels (480p).
Don’t get me wrong, SD is still relevant. But it’s not preferred for footage that needs higher detail. You can use SD for movies with a classic look or text-based clips. It is also a good option for online videos, as it doesn’t take much time to load on slow or poor network connections.
You may have seen it listed in the quality options of streaming and video-sharing platforms like YouTube.
HD or High-definition
Then comes ‘high definition’, which is 1280×720 pixels (or 720p). This is now the most common type and is perfect for most modern-day monitors and regular-sized flatscreen TVs. Obviously, HD has more pixels than standard definition videos, so there is much more visual detail. Since most devices support it, the SD size has mostly gone out of use.
You can even say that HD is now the new standard resolution for videos.
Full HD or Full High Definition
Full HD is 1920×1080 pixels (1080p) or 1920×1200 pixels. At present, this is the most common setting for smartphones, although they can also play clips of lower quality.
UHD or Ultra High Definition (a.k.a 4K)
Ultra HD, or the 4K video resolution, is rich in visual detail as it has a pixel count of 3840×2160 or 2160p (four times more than Full HD). The difference may not be noticeable to viewers, as not many have 4K televisions or monitors, but it makes a very big difference to video editors.
More pixels and detail mean there is more room to work when editing and zooming in. That’s why Ultra HD is the best resolution for video editing processes like color grading, graphics, and theatrical releases.
8K or Full Ultra HD
The FUHD or 8K has a pixel size of 7680×4320 and is more suitable for movies or projects that require the footage to have a theatrical feel. Despite the high visual quality it offers, 8K is not a widely used setting, although it’s great for editors as they have even more detail to work with.
These are just some of the commonly accepted video resolutions, but you can set any pixel count outside of the ones we’ve mentioned above. It simply depends on what your project requires and your artistic expression and taste.
Recommended resolution for aspect ratios
The resolution, ideally, should be according to the aspect ratio. Each aspect ratio, like 16:9, for example, requires a certain specific number of pixels in each frame for the visuals to be clear and crisp. Here are the resolutions that are advised for common aspect ratios that are used today.
| Resolution | Aspect ratio |
|---|---|
| Standard Definition (480p) | 4:3 |
| High Definition (720p) | 16:9 (the most common aspect ratio online) |
| Full HD (1080p) | 16:9 |
| Quad HD or 2K (1440p) | 16:9 |
| Ultra HD or 4K (2160p) | 1:1.9 |
| Full UHD or 8K (4320p) |
16:9 |
Why is resolution important?
Knowing what kind of quality setting to use for your videos is an important part of the planning process. What resolution you use will depend on the aspect ratio (format) required by the platform or device on which it will be played.
The main reason to make video resolution a priority is the direct effect it has on the clarity of the visuals. With a high enough resolution, you get more pixels to work with, so you have sharp footage with fine details for easy editing and viewing.
Low-resolution settings deliver okay-looking clips in small sizes. But when you try to increase the size, they will appear pixelated and blurry. So, use the best possible quality setting when you film and make the adjustments according to the platform later.

